POSTMAN BEST PRACTICES
API Test Automation
Building quality APIs has never been more important. At Postman, we believe being API-first is the key to innovation in the AI era. We built Postman Best Practices to share the foundational ideas Postman is built on and enable you to do your best work.
You can't build reliable distributed systems without comprehensive API testing, and you can't scale testing across teams without systematic automation and processes that enable collaboration rather than blocking it.
In this chapter, you’ll learn how to eliminate coordination problems that allow regressions to slip through when tests are scattered across tools and teams, and build automated workflows that catch issues before they reach production—whether serving human users or AI agents.

Abhinav Asthana
Postman CEO and Co-founder

Ankit Sobti
Postman Field CTO and Co-founder
As developers shift from writing code to higher-level tasks like system design and building more complex architectures, testing becomes even more critical. API testing is a continuous process that occurs alongside any modifications to the API's behavior, such as changes in the codebase, components, infrastructure, or dependencies.
When tests are scattered across tools or teams are working from different artifacts, it’s easier for regressions to slip through and integrations to break. The problem compounds when you have AI agents interacting with your APIs.
API testing in Postman
Postman provides a robust set of tools for API testing and quality assurance:
- API client to construct requests and observe responses
- Extensible Javascript-based testing environment to write validations and test scripts
- Automation environment accessible via app UI and CLI
- Performance testing tool to simulate the API under bigger loads and real-world usage patterns
- Mock servers to help isolate dependencies
- Interceptor tools to capture APIs from end-user applications
- Synthetic monitoring tool to help run tests post-deployed on automated alerts
- API specification management for centralized governance
- Visual workflow builder for creating low-code API orchestrations and complex testing scenarios
- Analytics and diagnostics tool to identify failing requests and analyze trends
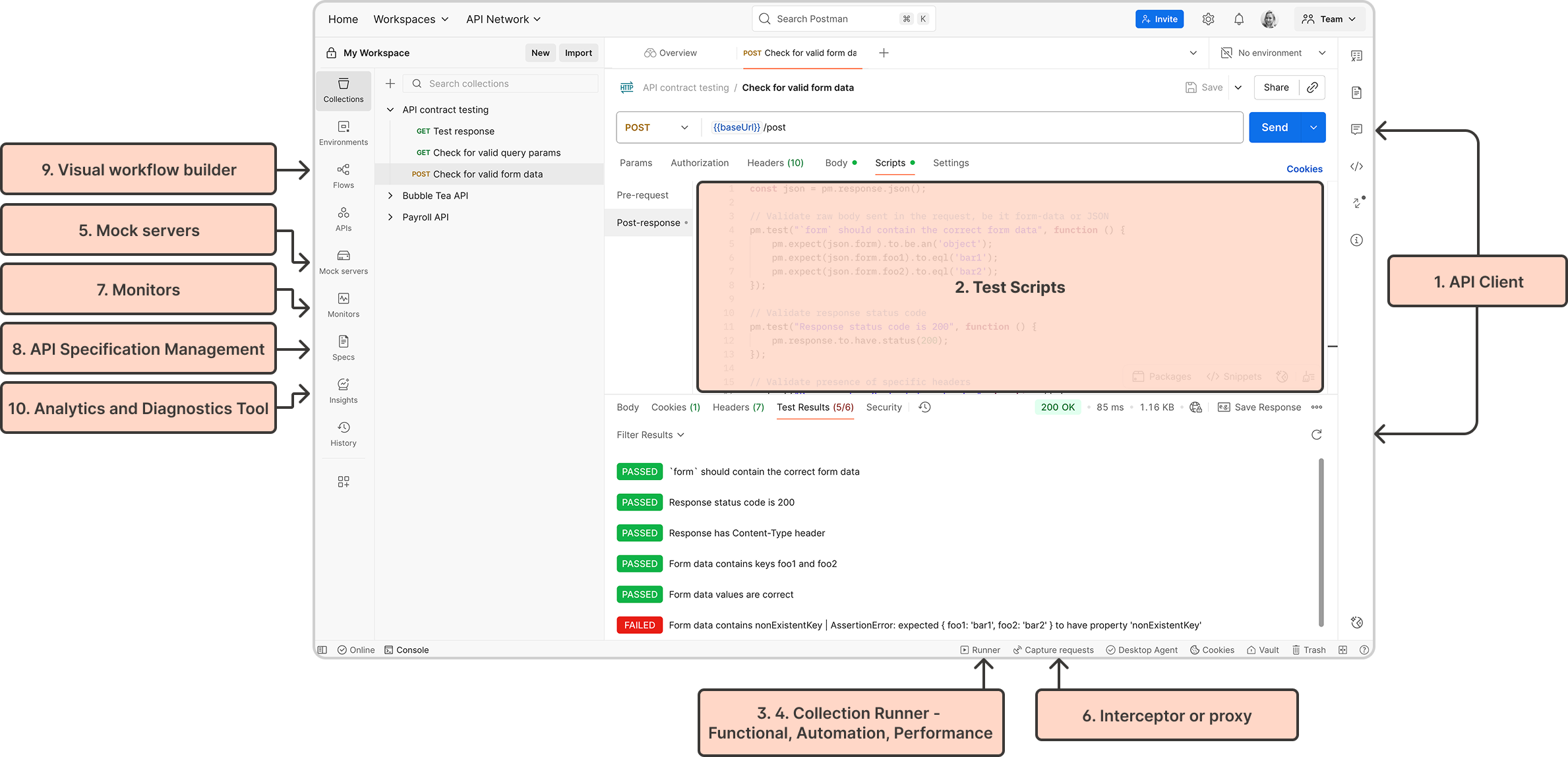
How API test automation connects with collaboration
Collections serve as executable documentation that captures what an API does, as well as how it should be used in practice. To support these goals, follow these recommended practices:
Testing involves many people who ship software: developers, quality engineers, security engineers, and SRE/DevOps. API testing is also needed by consumers of APIs, whether they're front-end developers or external users.
Anyone on your team who is involved in testing APIs needs to know what each API is, the intended and unintended use cases, and how to tie this information to the end goal. Postman Collections provide the core language for developers to communicate this.
Recommended practices
- Name collections and requests clearly to show the business purpose. For example, 'User Onboarding Flow’ rather than 'POST /users.’
- Provide realistic example request bodies and expected responses to help other developers understand data formats and edge cases.
- Write tests that validate both happy path scenarios and error conditions, showing what ‘success’ looks like.
- Use request descriptions to explain why certain parameters are required or what business rules apply.
- Set up environments that demonstrate how the API behaves across development, staging, and production contexts.
When teams follow these practices, collections become the shared vocabulary that aligns API producers and consumers on what the API contract actually means. Postman's test automation tools extend the ability of collections to testing, and when these are made available in workspaces, developers know exactly what to do.
If your team is adopting Postman for test automation, these tests can live inside their team-specific spaces, as described in Postman Best Practices for Internal API Collaboration.
Types of API testing
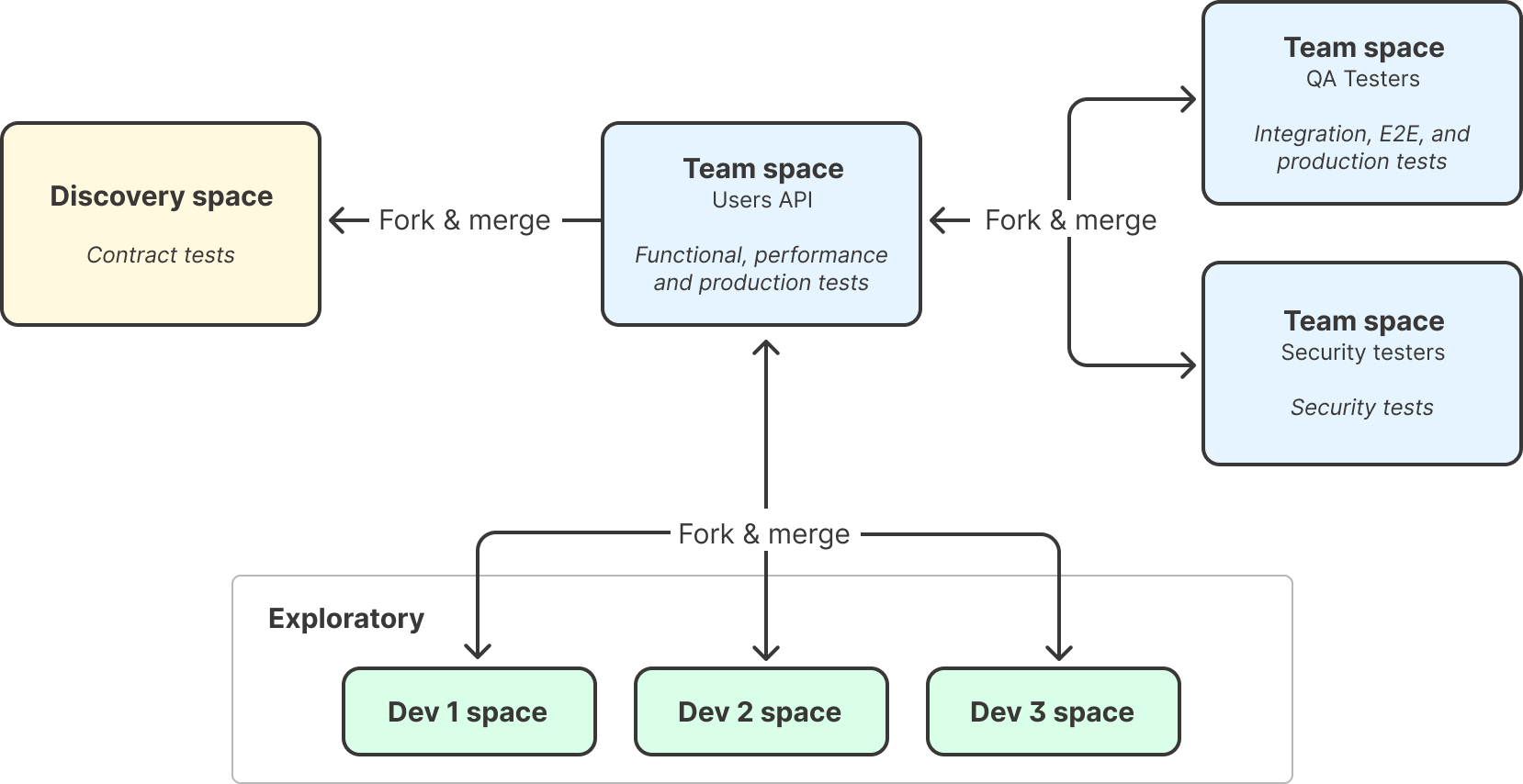
Development and validation testing
These tests are conducted by developers and QA engineers during active development to catch issues early and validate that APIs work as intended before moving to integration testing.
| Tests | Purpose | Recommended practices |
|---|---|---|
| Exploratory tests | Exploratory tests are informal tests conducted to explore application functionalities without predefined test cases. The goal is to identify defects and gain a better understanding through hands-on experience. Exploratory testing encourages testers to use their creativity and intuition to discover issues that may not be covered by scripted tests. |
|
| Functional/smoke tests | Functional/smoke tests verify that basic application functionalities work as intended, checking critical paths for important features. |
|
Integration and workflow testing
QA teams and developers perform these tests after individual components have been validated. These tests ensure that different services work together correctly and that complete business processes function end-to-end.
| Tests | Purpose | Recommended practices |
|---|---|---|
| Integration tests | Integration tests focus on interactions between different modules or services, ensuring integrated components work together. |
|
| End-to-end workflow tests | End-to-end workflow tests validate complete application flows from start to finish, simulating real user scenarios. |
|
Security and performance validation
Security engineers, DevOps teams, and performance specialists conduct these tests to ensure that APIs can safely handle production loads and resist attacks. Performance testing is especially critical for automated consumers like AI agents or other systems that require low latency or high throughput.
| Tests | Purpose | Recommended practices |
|---|---|---|
| Security tests | Security tests identify vulnerabilities and assess security measures to protect data and resist attacks. |
|
| Performance tests | Performance tests evaluate responsiveness, speed, scalability, and stability under workloads. |
|
Production monitoring
These tests are run by SRE teams, DevOps engineers, and platform teams to continuously validate that APIs work correctly in live environments and catch issues before they impact users.
| Tests | Purpose | Recommended practices |
|---|---|---|
| Synthetic production tests | Synthetic production testing involves automated tests simulating user interactions in production environments. |
|
| Consumer-driven contract tests | Consumer-driven contract tests ensure interactions between service consumers and providers meet consumer expectations. They focus on contracts defining how services should behave, enabling better team collaboration and ensuring changes don't break expected functionality. |
|
Recommended testing types across different API patterns
Testing patterns are mostly similar for app-specific APIs and reusable APIs. Contract testing helps producers and consumers align and enforce tests that catch breaking changes.
| Testing Type | App-specific APIs | Reusable APIs | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Exploratory | Required | Required | Critical for all API development |
| Functional/Smoke | Required | Required | Foundation of API reliability |
| Integration | Required | Required | Validates component interactions |
| End-to-end workflow | Required | Required | Simulates real usage patterns |
| Security | Recommended | Required | Higher stakes for shared APIs |
| Performance | Recommended | Required | Load testing is essential for shared APIs |
| Synthetic monitoring | Recommended | Required | Continuous validation in production |
| Contract testing | Optional | Required | Critical for multi-team dependencies |
See how WGU reduced testing time by 50%, cut back on meetings, sped up development with automated testing."
General guidance for testing
- Maintain tests in a shared internal workspace within a team
- Use environments to parameterize tests for different environments
- Use the Postman CLI to run tests in CI/CD environments
- Connect tests to your GitHub repo using git integration
- Connect Postman Monitors to existing engineering dashboard systems
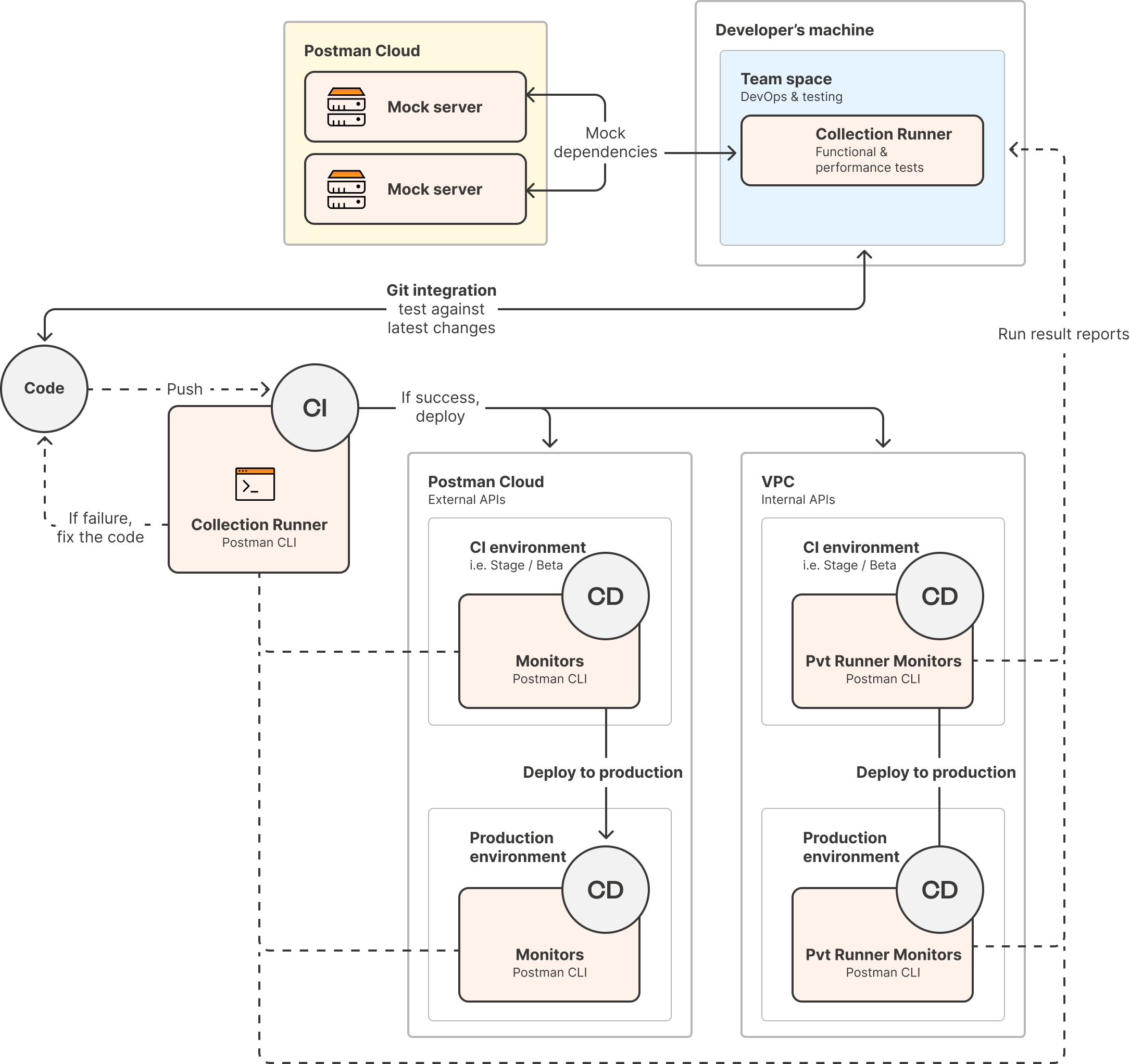
Recommended workspace topology
When implementing contract testing across teams, organizing workspaces is critical for maintaining clear ownership while enabling collaboration. The following workspace structure supports both automated testing workflows and team coordination, ensuring contract tests can run effectively in CI pipelines while providing visibility to all stakeholders.
| Workspace | Who owns it | What lives there | Access model | Why it matters for testing |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Consumer team workspace | Mobile, web, or backend consumer team |
| Internal team editors | Allows the consumer to evolve the contract with their codebase |
| Producer workspace | API team |
| Internal editors (consumers are usually view-only) | Keeps active development work separate from contracts but still visible |
| Shared contract workspace | Jointly owned, or by the Platform team | “Source-of-truth” fork of every consumer contract and badges for the last CI run |
| Central place where CI pulls contracts and both sides inspect failures |
| Partner Workspace | Platform team |
| External partners invited as guests | Gives external companies secure, read-only, or controlled-edit access without exposing internal assets |
| Private API network | Org-level enablement team | Index of all stable, reusable APIs, auto-published from producer workspaces | Everyone in the org | Enables new consumers to quickly discover the contract collection before writing code |
Ready to get hands-on? Get started with API testing templates →
